Language Development in Children
Components, Requirements and Milestones
Page 1. ... Page 2. ... Page 3. ..
Components of language development
- Communication, which involves combination of several cognitively learnt behaviors and skills.
- Phonology implies the ability to produce specific sounds for specific words: Speech development.
- Semantics refers to the correct use of the words to express specific thoughts.
- Syntax is the appropriate use of grammar to make sentences.
- Pragmatics defines the ability to communicate effectively with the skills that go beyond the basic understanding of the words and the rules of grammar. It demands child’s awareness of the social aspects associated with effective communication, such as -
i. ) Relationship with the partner one is conversing with.
ii. ) Social context in which the conversation is taking place.
iii.) The environment at large.
Requirements for language development
1. Language includes expressive and receptive functions:
- Vocabulary.
- Molding the words into their root forms.
- Sentence formations with understanding of grammar application.
- Modify the sentences depending on the situations.
2. Speech, the ability to produce intelligible sounds:
- Articulation effectiveness comes with well coordinated movements of the tongue, lips, and jaw muscles.
- Phonation: The voice production depends on effective functioning of vocal cords.
- Fluency of speech requires timely synchronization of phonatory and articulatory muscle groups with efficient interaction between speech and language skills. Its compromise leads to stammering/ stuttering in a child.
What is receptive language development?
- Receptive language includes hearing and understanding.
Right from time of birth, newborns demonstrate preferential response to human voices over inanimate sounds. - Over the first 3 months infants begin to recognize the parents’ voice, which has a noticeable calming effect on a crying baby. The preference to human voices points at the infant’s efforts towards development of receptive language.
- At 9 months of age the infant begins to participate in few verbal exchanges that are directed towards him.
- The progress continues and by 4 years of age, children can follow adult conversation. They can also answer simple questions from a recently heard short story.
- At 5 years of age, children develop receptive vocabulary of more than 2000 words and are able to follow 3-4 steps commands.
Liked what you read just now? Pay it forward!
Have Questions? Ask the Expert and have Your Answers for Free
What is expressive language development?
Expressive abilities include talking, writing and other forms of symbolic expressions.
Cooing sounds
Cooing sounds that an infant makes in the second month of life is infant's first step towards development of expressive language.
Symbolization
Symbolization of a 3 months old infant’s different vocal sounds are interpreted by parents as pleasure, pain, fussing, tiredness, and so on. Thereby, 3 months of age onward most infants can maintain social interaction by vocalizing in a reciprocal fashion.
Infants at 5 months of age laughs expressively in response to a pleasant interaction and may even respond with monosyllables.
Vocabulary development
Over the next several months, infants learn 1 or 2 words that represent common objects used in their day to day life.
Pronunciations
Children readily adopt adult pronunciations. They imitate words used by their parents, siblings and others. One year old child begins to make spontaneous corrections to his own pronunciations and aligns them with that of his language experts. After a lot of practice over a period of time the child establishes a stable 10 or more words vocabulary.
Interactive language development
The parents who reinforce their children’s attempts to communicate and are sensitive to their current interests enable them to more readily associate verbal symbols with their external referents.
Learning grammar
Children intensely observe the pragmatic principles and learn the conventions for language use. Thus their expressive skills steadily increase and mature.
By 4-5 years of age, children are able to carry on conversations using grammatically correct sentences that are descriptive enough to provide the necessary details.
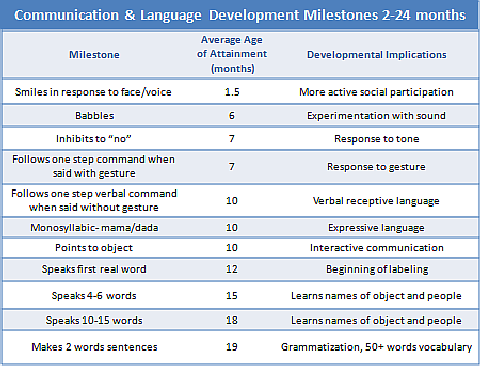
Milestones of language development
The milestones of language development are the same across all languages and cultures of the world. However, some minor variations may be noticed at times depending on the complexity of the grammatical structure of individual languages.
Have Questions? Ask the Expert and have Your Answers for Free
Analytic and holistic patterns of language learning
Both analytic and holistic pattern of language learning are essential for normal development of language.
- Analytic is the commonest learning pattern.
In this form of language learning, a child learns analytic skills from simple to more complex and lengthy forms. - Holistic language learning pattern (Gestalt learning pattern)
In this pattern, children memorize familiar phrases and repeat them in a generalized fashion. Consequently. the sentences often reflect inadequate knowledge of grammar.
However, these children gradually learn to break down the meanings of phrases. They gradually learn to apply their analysis skills to the sentences. As a result the communication sounds more original and the child is able to assemble his thoughts in a more flexible manner.
Middle childhood development polishes children's ability to communicate effectively and psychosocial development.
We are on page 2 of "Development of Language in children"
<<<Language Development: Previous Page
Children's communicative capabilities.
Language development : Next Page >>>
Factors affecting development of language in children
For more related pages please scroll through the right column of the page.
Back To
Process of Childhood Development
Liked what you read just now? Pay it forward!
Can't find answer to your concern? Search the site!


Follow Me
Liked What You Just Read?
Pay It Forward!
Related Pages
|
Neuronal plasticity Development Stages Physical Domain Cognitive Domain Language Development Social and Emotional Early Development Prenatal Neonatal Period Infancy and toddlerhood Early Childhood Development, Logical thinking Intelligence development Information processing Attention span Memory strategies Communication capabilities |
Liked What You Just Read?
Pay It Forward!
|
Motor skills development process Gross motor skills Fine motor skills Influencing Factors Nativism versus empiricism Types of Intellectual structure Stages of cognitive development Milestones of cognitive development Cognitive disorders What is language development Building communicative abilities Components Requirements Receptive language Expressive language Milestones of language development Patterns of learning language Factors affecting language development Milestones charts Causes of delay & deterioration Speech Fluency Components of Stuttering Developmental Dysfluency Causes of Exacerbation Psychological Implications Incidence Treatment |
Liked What You Just Read?
Pay It Forward!







New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.