Itching in Pregnancy
Can Be Devastating for The Baby
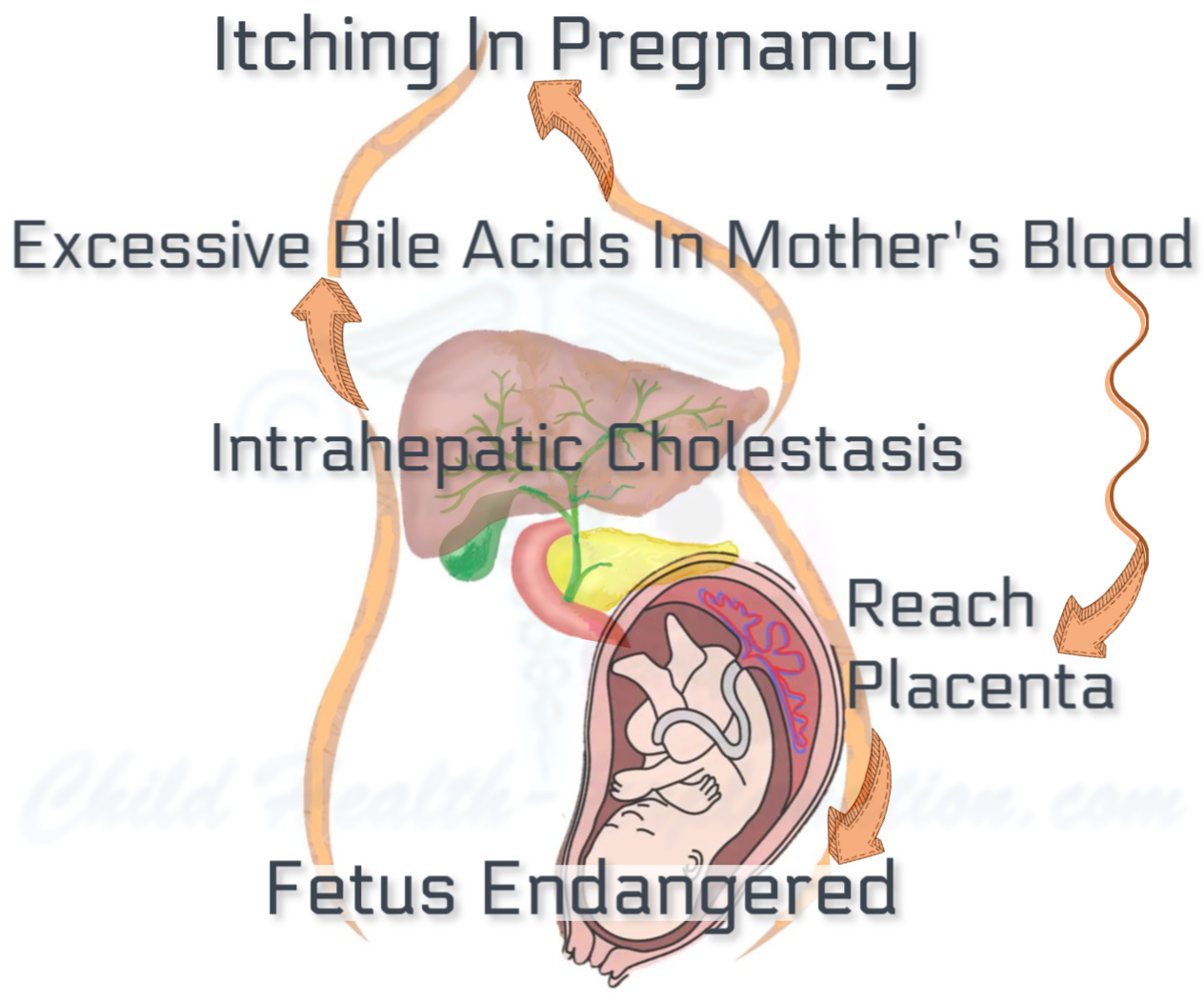
Itching in pregnancy is commonly ignored as a normal effect of pregnancy induced changes in the body but is certainly not normal. It is the sign of intrahepatic cholestasis, the unique liver disease of pregnancy.
Cholestasis of pregnancy
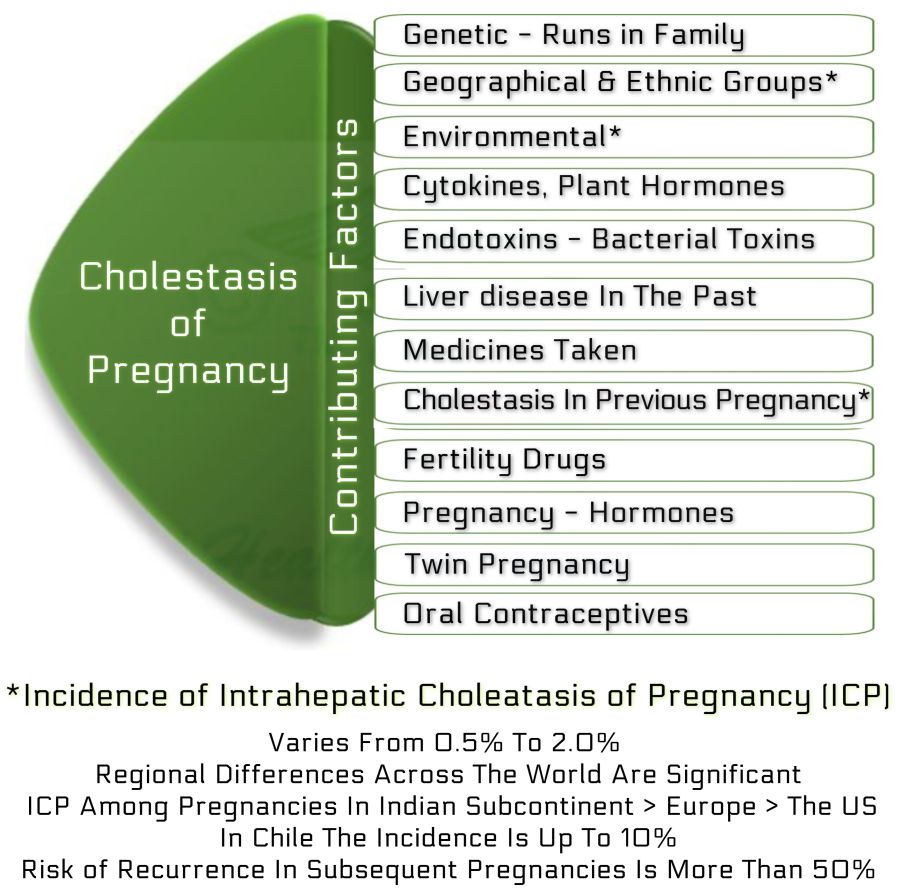
Cholestasis of pregnancy is an innocent self-limiting liver disorder as far as the mother is concerned, but a cause of several fetal complications. It usually begins towards the end of the second trimester of the first pregnancy and resolves spontaneously in the second or third week after childbirth.
The disordered physiological processes of the disease
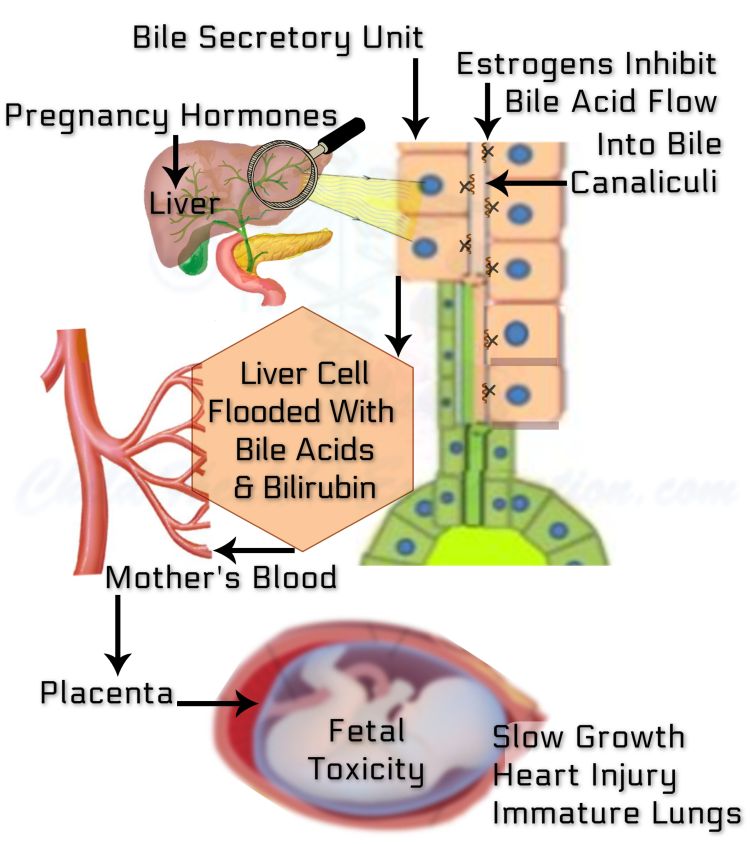
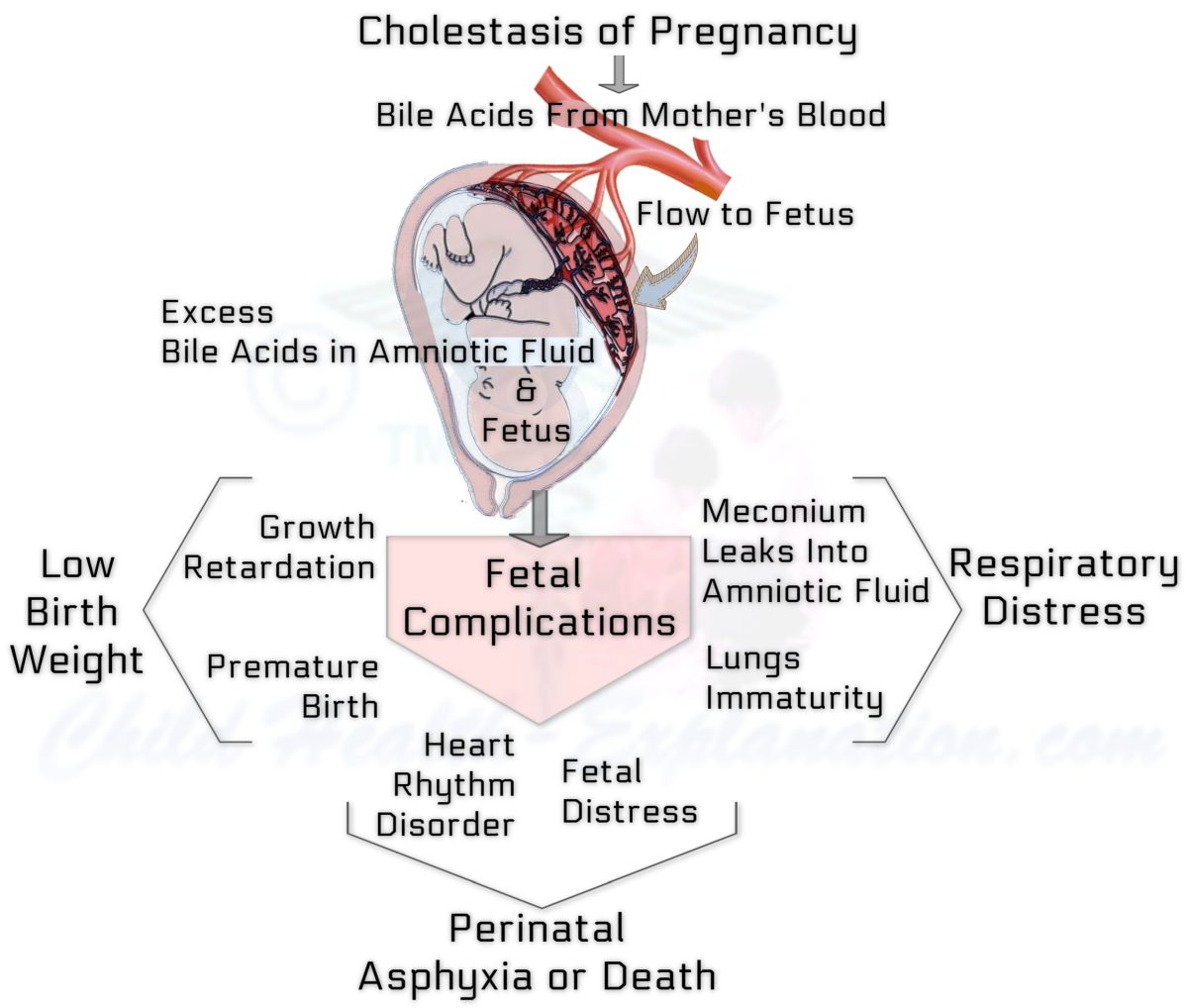
Pregnancy hormones affect liver function. Of them, mainly estrogen hampers bile acids export out of their site of production, the liver cells. As a result, the accumulated bilirubin and bile acids are unable to flow out of the liver cells into tiny collecting ducts, the canaliculi. Instead, they spill into the bloodstream, and then through the placenta to the fetus. Bile acids and bilirubin, both are toxic to the fetus.
Diagnosis
Liver functions test in the mother's blood
A single blood test, the mother's liver functions, is all that is required to clinch the diagnosis. Bile acids concentration of 10 μmol/L or above confirms intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy.
The increase in serum concentration of bile acids is the first, and often, the only abnormality noted. The blood test may, however, show generalized functioning disorder of the liver in the form of elevated liver enzymes - AspAt, AlAt, and GGTP.
Itching in pregnancy, the key symptom
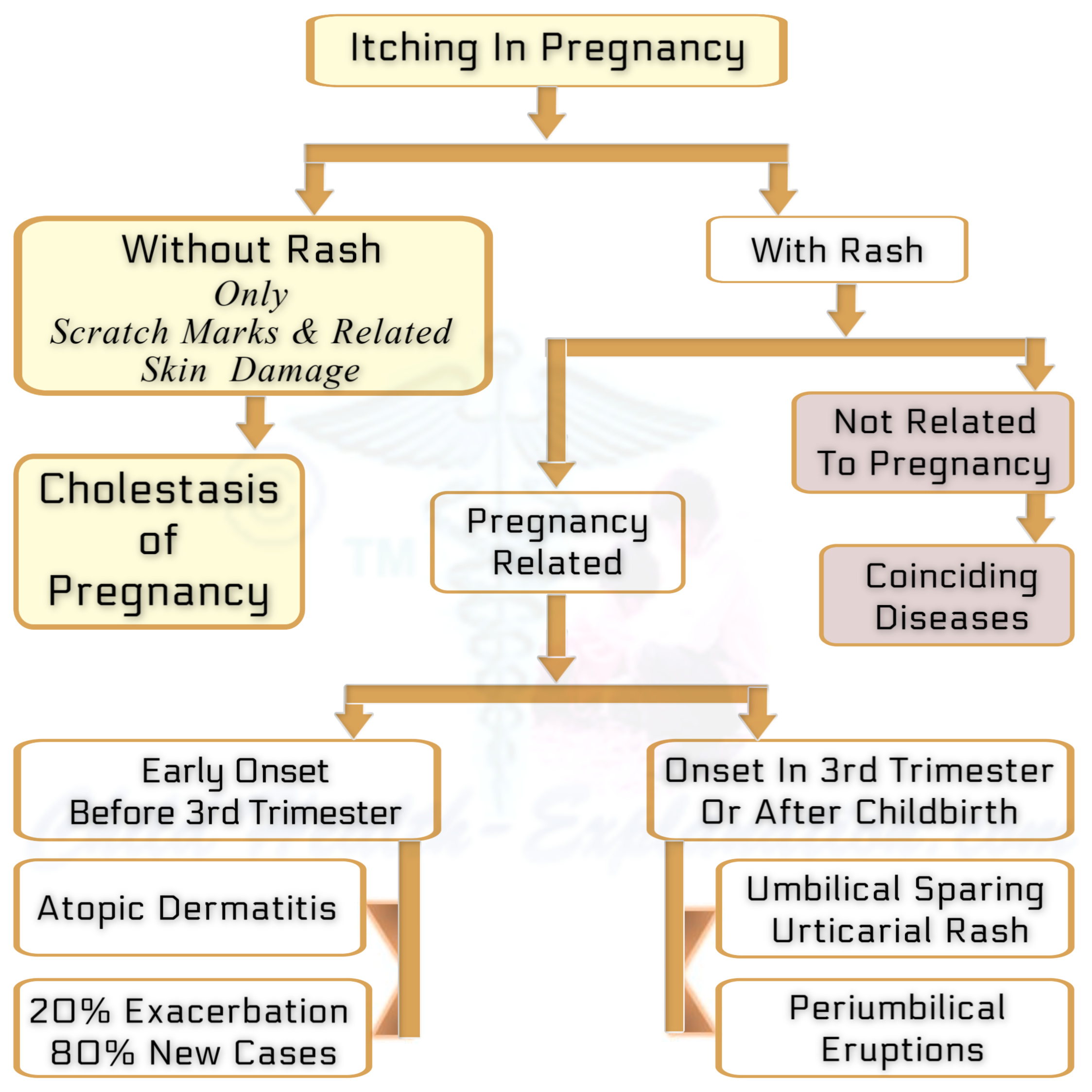
Unaware of the danger high bile acids in mother's blood impose on fetal growth, most women don't even bring the only symptom they have to the notice of their doctor, itching in pregnancy - typically in hands and feet.
For Atopic Dermatitis - click here
And here for Umbilical sparing urticarial rash as cause of itching in pregnancy
Pruritus, without any skin rash, is not the only symptom of cholestasis of pregnancy. There are many more. They all point towards compromised functioning of the liver, for example, poor appetite, indigestion, fatigue, light-colored stools, and slight yellow discoloration of eyes, skin, and urine. But they too get overshadowed by the discomforts of advanced pregnancy.
However, the signs and symptoms in the pregnant woman do not correlate with the severity of fetal complications.
Itching in pregnancy
An unborn baby's way to alert the mother
High bile acids in mother's blood endanger the fetus. The gravity of fetal complications correlates well with the bile acids level in the mother's blood.
Serum bile acids level above 10 μmol/L in women with cholestasis of pregnancy increases the risks of overall adverse perinatal outcomes. And, if it rises above 100 μmol/L or more, the chances of sudden intrauterine fetal death increase by several folds, that too just before birth, or during the birth process itself. Nevertheless, in a large number of the cases with bile acids concentration between 10 and 40 μmol/l, the fetus may remain unharmed.
The same does not hold true when the blood bile acids level rise above 40 μmol/l. Beyond 40 μmol/l, the magnitude of the risk to the baby's well being, and its need for intensive neonatal care is directly proportional to the mother's bile acid levels.
Almost 2 in 15 infants born to mothers with intense itching in pregnancy require to be cared for in the newborn care unit for inadequate fetal growth, premature birth, fetal distress, falling frequency of fetal heartbeats, presence of meconium in the amniotic fluid, respiratory distress syndrome, or birth asphyxia.
What causes fetal complications?
Exactly how cholestasis of pregnancy causes fetal complications is yet not quite clear. It all translates into bile acid toxicity. A high concentration of bile acids in fetal blood aggravates the activity of almost all smooth muscles.
- It makes the uterus much more sensitive to oxytocin, which threatens preterm birth.
- The contraction of blood vessels on the fetal side of the placenta jeopardizes its supply of oxygen and nutrients, thereby the optimal fetal growth and development.
- Increased propulsive movements of the large intestine of the fetus cause the passage of meconium into the fluid surrounding the fetus.
- It provokes cardiac arrhythmias and impairs the ability of the heart muscle to react to the stress of labor. Consequently, blood flow to the fetus gets severely compromised, leading to fetal hypoxia and eventually death. Treating doctors, therefore, opt to deliver a premature baby.
Click here to know more on bile acids that cause itching in pregnancy and devastating fetal complications. - scroll down a little. On your right hand side you will find the link for the video "Overview of Cholestasis" - watch it, and have a clear picture on what goes on inside the liver.
Back To
Fetus: Growth Stages and Viability
Liked what you read just now? Pay it forward!
Can't find answer to your concern? Search the site!


Follow Me
Liked What You Just Read?
Pay It Forward!
Related Pages
|
Development Fetal Viability Morbidity & Mortality Mother's Nutrition Folic Acid Supplementation Limitations Uterine fundal height Ultrasound evaluations Causes for concern Causes of large for date baby Causes of small for date baby Stress and fatigue Sleep and snoring Spacing pregnancies Infections in mother Placenta Do's and Don'ts Obesity in Mothers Hampers ..... Severity groups of FAS Incidence Mode of effect on fetus Effects of alcohol on fetus Preventive? Yes Treatment - only supportive Mothers Who Drink Alcohol Beware Why restrict? Caffeine & newborns' aponea Mode of effect on fetus Effects on mother's nutrition Mother's blood circulation Decaf coffee |
Liked What You Just Read?
Pay It Forward!
|
Thyroid hormone Iodine supplementation Insulin Insulin like growth factor Prostaglandins Glucocorticoids Mother's exposure to tobacco smoke Harms baby in the womb Hinders effective breastfeeding |








New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.